The Benefits of Making Your App Work Offline

The Benefits of Making Your App Work Offline
Discover the benefits of creating an app that works offline, including more streamlined UX and greater customer loyalty.
Most of the time, apps work best when there is a fast data connection or WiFi.
There are many instances where users can benefit from an app that works well offline, though. Consider commuters who may spend significant time in subway tunnels, or travelers who don’t always want to pay a hefty price for international data.
Poor connectivity can result in a poor user experience. Apps with poor UX are frustrating, and many users may simply choose to delete them.
So, how can you make part of your app available without an internet connection?
We explore how apps work, the benefits of offline-first apps, and some examples of apps that have successfully leveraged offline capabilities.
How Do Most Apps Work?
Most apps use a simple cycle of data transfer, which includes the app on one side and the content from a server on the other side. These two should talk to each other to ensure a smooth transfer of data anytime it’s needed.
You might think that e-commerce apps or photo stocks need to be online all the time and might slow down whenever the internet connection is slow.
However, if the apps are “offline-first,” they will not slow down when connectivity is poor.
What are the Benefits of an Offline App?
Why should you make an app that works offline? The benefits are numerous:
Poor Connectivity Won’t Frustrate Users
If you have an “offline-first” app or an app that can partially function offline, then it’s more likely to be used in areas of poor connectivity.
Make sure to consider where your potential users are going to be during the day. Ask yourself if people using your app are residing in an area with limited WiFi or data connectivity. If so, making your app work offline can help you increase your user acquisition and retention rates.
You Will Have an Edge on the Competition
The app market is huge and there is often at least one competitor per app. Consider Uber and Lyft, or WhatsApp and Facebook Messenger.
People usually choose apps based on a number of factors. Some of them opt for a better functionality, while others appreciate top-notch UX/UI design.
But what if your competitor is an online app while you are offline? In no-network zones, you have a greater chance of winning over the competition.
Gain More Loyalty from Users
If a user knows they can trust your app in areas of poor connectivity, they will become more loyal.
Users also appreciate apps that work offline due to the following:
- Users want an app that works instantly and without any delays or difficulties.
- Users can make changes to their data, regardless of an internet connection.
- When stored locally, the data has little to no chance of getting breached.
- Offline apps require very little loading time.
- Offline apps are less likely to drain your battery. Note that 49% of millennials consider an app with high battery usage to be a deal breaker.
Examples of Offline Apps
There are various offline apps which make people’s lives easier, their work more productive, and their time more efficient.
Netflix Allows Users to Be Entertained Anywhere
In late 2016, Netflix announced that it would allow users to download some of their most popular TV shows and movies to store locally on their devices.
Streaming video requires a high-powered internet connection. While an average internet connection can suffice for most apps, this isn’t the case for Netflix.
Allowing users to download content ensured that Netflix would still be used in areas of poor connection, or by people with smaller data plans.
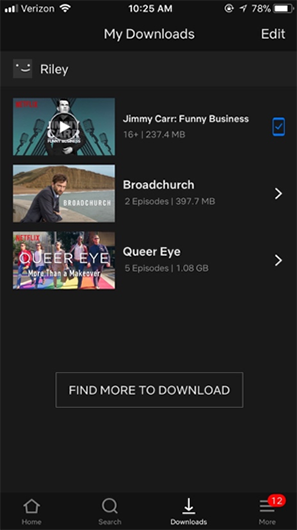
Anyone can download Netflix’s content while on WiFi and then feel comfortable watching their videos anywhere.
Google Maps Gives Travelers’ Peace of Mind
A map app must at least partially work offline, given how often users access them when traveling.
Google Maps allows users to download a pre-determined area of their worldwide map. Then, users can access their detailed maps and directions anywhere.

Most phones’ GPS systems work even with no internet connection. Therefore, users can navigate on Google Maps even with absolutely zero internet connection.
Offline Access Benefits Your App
It’s understandable that certain apps cannot be made fully offline. However, most of them can choose to make at least a portion of their data accessible with no internet connection.
Allowing an app to work offline ensures better UX, a leg up on the competition, and greater customer loyalty.
