Benefits of Cloud Computing in Healthcare
Benefits of Cloud Computing in Healthcare
Cloud adoption is growing rapidly across most industries, providing professionals with a fast and reliable way to communicate data between essential systems. Cloud solutions allow healthcare providers to update patient records and adjust treatment plans in real-time, though as data becomes more accessible, the threat of sophisticated cyber-attacks may also increase.
Cloud technology has forever changed the way many modern industries operate. By providing teams with bespoke systems designed to streamline essential processes, improve efficiency, and ensure reliable scalability.
One such industry is healthcare. Data published in 2023 reveals that 70% of IT professionals working in healthcare have already adopted cloud computing solutions, with a further 20% intending to migrate to the cloud by 2025, contributing to a potential cloud adoption rate of 90%.
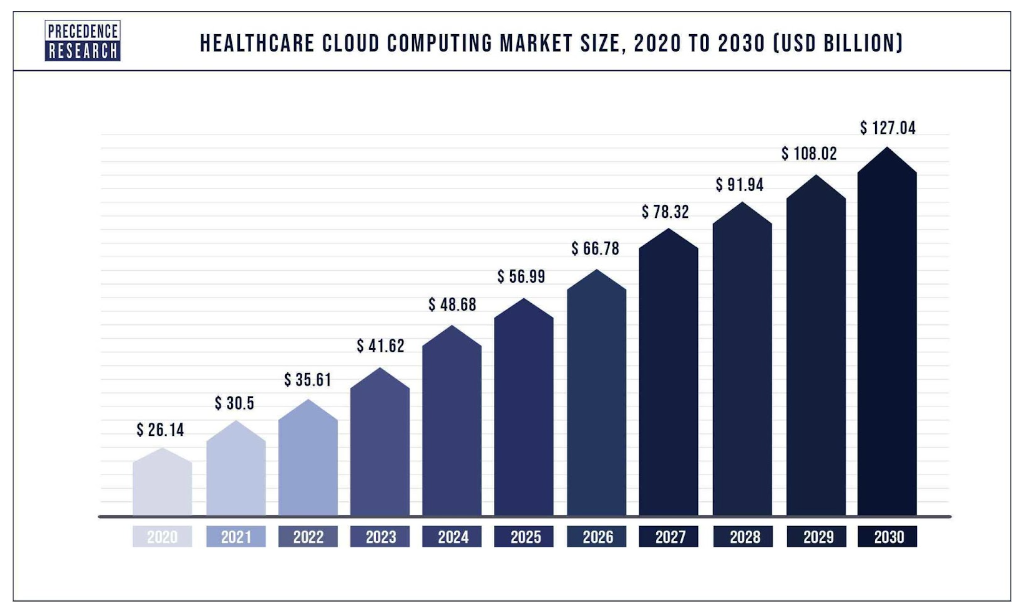
Source: Precedence Research
Though the development of cloud-based systems can bring several significant benefits to healthcare providers, ultimately assisting staff in improving service quality, healthcare teams are bound to strict privacy and data security regulations that can complicate cloud developments.
To help healthcare professionals create safe and reliable cloud solutions, this article will explore healthcare in the cloud, including how providers ensure data security in modern systems.
Ready to jump to the cloud? Connect with the best cloud consulting companies on The Manifest.
How Cloud Computing Benefits Healthcare Providers
Modern healthcare professionals are expected to store and analyze massive amounts of sensitive data of thousands of patients. This means any way to simplify the way teams access and share important records can contribute to dramatic service improvements.
By developing and implementing cloud-based solutions, professionals can ensure all patient records are stored in one place, with files made accessible to specialists regardless of physical limitations. This means live data can be freely analyzed and shared between doctors and experts across multiple facilities, improving the speed and efficiency of treatment programs.
Additionally, cloud-based solutions allow healthcare institutions to automate key processes. Providers can automate scheduling, claims, billing, and registration processes, while pharmaceutical companies can automate the manufacturing and distribution of vital medication.
However, as records are made more accessible, the threat of data breaches and cyber-attacks can increase. Suppose cloud-based systems are not designed in line with cybersecurity best practices and are frequently updated by IT professionals. In that case, healthcare professionals may increase the risk of sophisticated cyber-attacks and find themselves in danger of breaching strict data privacy rules.
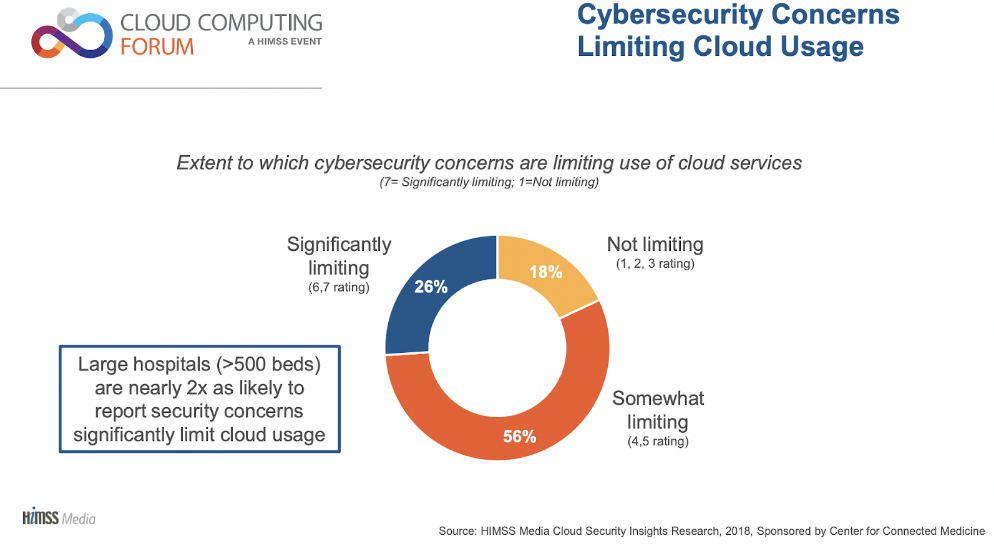
Source: HIMSS
Healthcare Cloud Security Challenges
Before exploring how healthcare providers can ensure data security within cloud-based systems, it’s important to understand the cloud security challenges modern professionals face. Below is a summary of the key challenges healthcare teams face transitioning to cloud-based systems.
- Compliance: Strict data privacy regulations such as the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) govern the way that cloud solutions may be developed, ensuring compliance can cause issues for teams as IT infrastructures are scaled
- Resource constraints: Many healthcare providers are expected to operate with limited IT budgets and restricted access to associated resources. This can influence the speed and efficiency at which teams are able to transition towards cloud-based systems
- Complexity: There is no one-size-fits-all approach to cloud development. With multiple environments and tools for teams to choose from, designing and implementing systems capable of integration with legacy tools can be a lengthy and challenging process
- Third-party issues: Bespoke cloud-based systems typically rely on integrations with third-party tools, software programs and components. Identifying and addressing potential security gaps between these components can cause issues for IT teams
- Continuity: Safely and efficiently migrating sensitive patient data to the cloud can be a resource-intensive process, often impacting daily operations. Some teams may struggle to allow for such disruptions for fear of negatively impacting service quality
- Data breaches: Data suggests cyber-attacks have increased by almost 40% globally in recent years, with the healthcare sector observing a 60% increase in attacks between 2021-2022. Cloud tools must be frequently monitored and updated to mitigate these risks
How to Improve Data Security in Cloud Environments
Though the design and initial implementation of cloud-based systems can create challenges for healthcare providers, the ability of these systems to improve wider operations is often too desirable to ignore.
Thankfully, IT teams working in the healthcare industry can follow a number of cybersecurity best practices to improve data security and protect against cyber-attacks.

Source: Maryville University
End-to-end Encryption
IT teams must ensure all communications and data transmissions sent within cloud systems are subject to end-to-end encryption. These programs convert sensitive data into an unreadable format which can only be decoded using a predetermined key. This prevents malicious actors from intercepting identifiable data in transit by restricting access only to authorized personnel.
Access Management
Access to cloud-based storage systems must be secured using managed access control systems. Policies must cover all systems, including cloud-based building security systems, patient data storage systems, and internal communications tools. Authorized staff must be issued personalized credentials to be monitored and reviewed by internal security teams.
Multi-factor Authentication (MFA)
Access control policies can be further strengthened using MFA policies. In addition to a primary access credential like a strong password, authorized staff must present additional credentials before access to sensitive data is granted. Other credentials can include a one-time access code sent to a secure email address, or a biometric indicator like fingerprint or facial scan. Experts believe MFA policies may be able to prevent up to 99% of cyber-attacks.
Data Backup Policies
All data stored in cloud-based systems should be backed up across multiple sources to ensure essential systems remain functional even during attempted breaches. Typically, a 3-2-1 rule will be implemented. This means three copies of each data set must be stored in a minimum of two separate systems, with one backup stored offsite to minimize the exploitable attack surface.
Frequent Updates and Maintenance
New vulnerabilities within popular software and hardware systems are exposed on a daily basis. To ensure cloud-based systems are not vulnerable to novel cyber threats, all systems must be updated and maintained frequently. Most cloud storage providers perform automatic updates as standard, but internal teams should still regularly assess systems to ensure no exploits remain.
Follow Cybersecurity Best Practices to Protect Sensitive Data in Healthcare
Cloud adoption rates continue to grow within the healthcare sector, as more institutions begin to understand the benefits of this technology regarding improving core services. However, as sensitive information becomes more accessible, data security policies must be strengthened to mitigate the risks associated with sophisticated cyber-attacks.
By following the cybersecurity best practices covered in this guide and ensuring IT and security teams are supported in developing cloud-based systems, healthcare providers can create bespoke and effective solutions while ensuring data security remains a top priority.
