5 Cybersecurity Best Practices to Safeguard Your Business Data

5 Cybersecurity Best Practices to Safeguard Your Business Data
In 2022 alone, the Federal Bureau of Investigation received 800,944 complaints from US businesses that fell victim to cyber attacks.
While it’s true that cyber-attacks are on the rise, your business doesn’t have to fall victim to an attack. On the contrary, you can take the initiative by implementing cybersecurity measures to safeguard against the many security hazards in cyberspace.
Here are five essential cybersecurity best practices you can implement to keep your business data safe.
1. Enable Two-Factor Authentication
Two-factor authentication (also called "multi-factor authentication") is one of the commonest cybersecurity best practices you can implement to keep cyber threats at bay. Companies like Microsoft and Google use it to keep their customers' data safe, and it's recommended by legislation like the European Union's General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR).
This simple cybersecurity measure can protect your business’s data by requiring that your employees provide a second authentication factor (other than their passwords) before they're granted access to their accounts. The additional identity-verifying information could be:
- six-digit one-time passwords sent to their phone number each time they log in
- their biometrics (e.g., a fingerprint, retinal scan, or facial recognition scan)
- the employee's voice
The quality that makes two-factor authentication effective is the extra layer of security it provides.
Before its implementation, usernames and passwords were all malicious actors needed to gain access to a business's data. Now, even if hackers manage to acquire your employees' usernames and passwords, they'll be unable to access the accounts without their phones or biometric data.
But that's not all: two-factor authentication can also alert you to suspicious activity as it happens in real time. In some cases, your employees will receive emails when unauthorized users attempt to log in with their credentials from an unrecognized device. The email may prompt them to confirm whether they recognize a sign-in attempt. See this sample email sent by Google to confirm a sign-in:
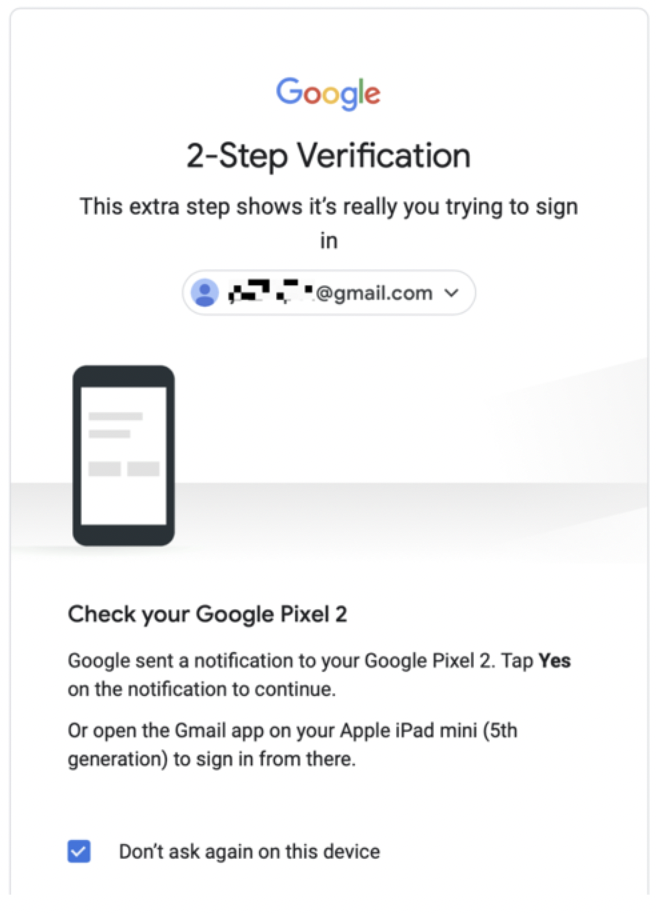
Consider using multi-factor authentication if you have a distributed workforce and your employees log in from devices outside your corporate network. This cybersecurity measure is straightforward to implement and won’t strain your cybersecurity budget.
2. Enforce Strong Password Policy
Cybercriminals employ several techniques like social engineering and brute force attacks when compromising employee accounts. Weak passwords increase their success odds and the likelihood that business owners like you will experience a security breach.
Thus, another way to keep your data safe from cybersecurity threats is to enforce a strong password policy in your workplace.
Enforcing a strong password policy involves creating a set of ground rules your employees will follow when setting passwords for their accounts. Typical rules may include using separate passwords for each account and creating strong, lengthy passwords that include a combination of letters (upper and lowercase), numbers, and symbols.
Incidentally, you’ll need to educate your employees about the criteria their passwords must meet to be considered strong. Search engine giant Google provides tips on how to set a strong password. It says you should:
- be unique (and not reused for an employee’s personal accounts)
- be memorable
- exclude common patterns (e.g., “1234”)
- exclude personal information (for example, a significant other’s birthday)
Passwords that meet the above criteria should work as a first line of defense against unauthorized access to your business’s intellectual property. If you want to be absolutely sure the passwords are hard to crack, ask them also to use this table as a guide when choosing:

Source: CDN
Be aware of the downsides of this cybersecurity strategy and the available remedies.
The main downside to having an employee use a complex password is that they may write it down and store the paper near their workspace. You can discourage this practice by deploying password managers that help them store and remember their passwords. These tools will also come in handy if you mandate that your employees change their passwords every three to six months.
3. Create Data Backup
Regularly backing up your data is wise from a business standpoint, but it's also one of the smartest cybersecurity best practices. The reason is that you can fall back on your data backups in the event of a ransomware attack.
Ransomware attacks are among the most common cyber attacks deployed by criminals during a security breach. They involve using malicious software (ransomware) to hijack the files on business computers and hold them for ransom. In 2022, ransomware was used in close to 68% of all the cyber attacks recorded worldwide.
While the hope is that your cybersecurity policies prevent employees from falling for ransomware, it only takes one click on a malicious link to turn into a security incident. Time management stats show that, on average, employees check their email every hour and 40 minutes. Since email phishing has been found to be the most common delivery method for ransomware and the emails sent look like legitimate ones at first glance, the likelihood that an attack occurs increases.
Check out this example of a phishing email sent to an employee:
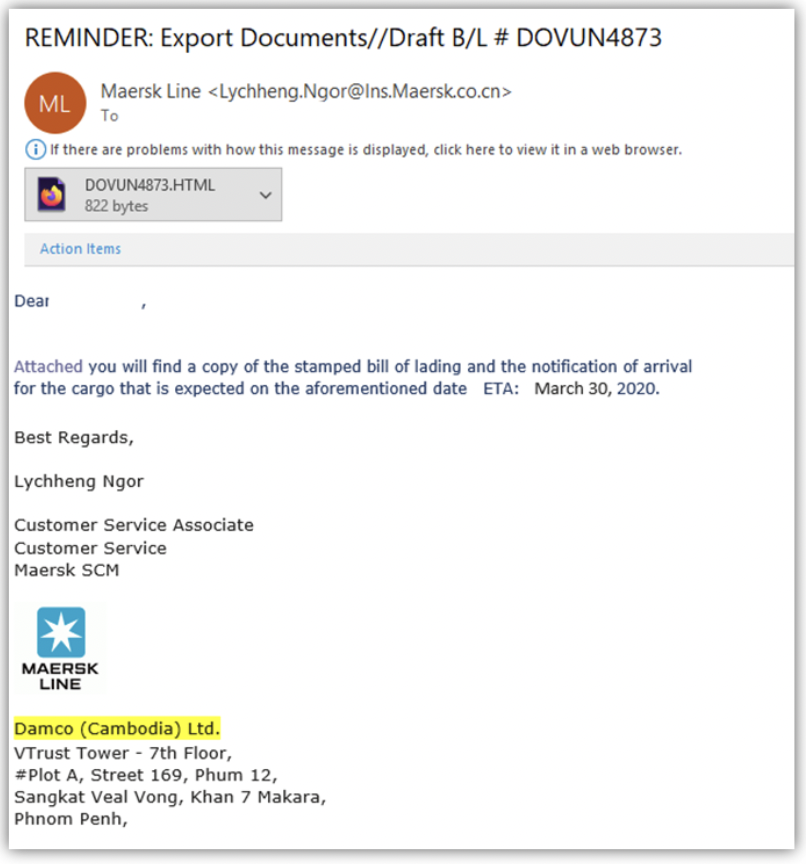
Source: Cheap SSL Security
The only way you’ll conclude it’s a phishing email is if you examine it thoroughly. Notice that the email sender is supposed to be Damco based in Cambodia. However, the sender’s email address domain registration was done in China (.cn). Then, there’s the use of the Maersk Line logo. That company, while legitimate, is based in Denmark.
Also, ask yourself, why would a customer service associate send an email that supposedly contains export documents?
Suppose unauthorized users gain access to your data after an unsuspecting employee clicks on a phishing email like the one above. In that case, regular backups will ensure that your business can run as normal.
As to how you can back up your business data, consider using the 3-2-1 rule. Have three copies of your data at all times. Back up two versions on separate storage devices and the final version offsite.
You have plenty of choices of physical backup devices. External hard drives (whether solid state or hard disk drives) and USB flash drives can work. Their storage capacity can range from 500 gigabytes to two terabytes and up. Also, optical media like DVDs or CDs are useful for storing smaller file backups.
As for offsite solutions, cloud storage is unbeatable. You can store your business’s files on a remote server and access them with an internet connection for a monthly fee. Services like Google Drive, OneDrive, and Dropbox are among the most popular.
4. Train Employees about Cybersecurity
You can also combat security vulnerabilities by educating your employees about network security.
Programs and courses that provide security certifications for beginners can help your employees learn. At the minimum, your employees will learn about phishing emails, phishing scams, and other tricks cybercriminals use to compromise critical systems. Additionally, they’ll learn how these cybersecurity breaches occur in the workplace and how bad actors exploit security gaps.
More importantly, your employees need to know how their actions can unwittingly aid malicious activity. For example, cybersecurity training can stress the importance of accessing company data through private networks and avoiding using public networks (e.g., the public Wi-Fi networks in coffee shops).
It's essential that you weave cybersecurity training into your business operations.
Rather than send the occasional email and organize training sessions every odd year, consider inviting cybersecurity professionals to speak to your employees at regular intervals.
You could even incentivize attendance of cybersecurity courses by making them part of your employees’ continuous development. When an employee is convinced that their cybersecurity awareness will help their career prospects and translate to job-ready skills, they may be more inclined to internalize and practicalize what they learn.
If you run a tech company, consider teaching your employees how artificial intelligence can help defend against AI-powered cyber attacks.
5. Conduct Regular Cybersecurity Audits
Conducting regular cybersecurity audits will help you identify security vulnerabilities and cybersecurity risks to your business.
A cybersecurity audit involves assessing your business’s security policies while attempting to discover any threats or areas of improvement.
During an audit, you’ll determine whether your business complies with cybersecurity regulations and evaluate your security posture, among others. More frequent audits will look into the validity of your antivirus software (i.e., whether it’s up-to-date). It isn’t uncommon to change a cybersecurity partner during the process.
There are two types of cybersecurity audits you can perform:
- Internal Audit: When you do an internal audit, your business’s cybersecurity personnel handles the checks. This type of audit is common with smaller businesses.
- External Audit: An external audit invites auditors who aren’t affiliated with the company to conduct the checks. Bigger companies typically choose these audit types.
How often you perform audits will depend on your business.
For example, if you store sensitive information on your computer systems, you’ll need frequent audits to ensure its safety. Whether or not the audit will be disruptive to business may also play on your mind.
Additional factors to consider when conducting audits include:
- Scope: How comprehensive do you want the audit to be? Should it give you the full picture of your business’s cybersecurity posture or focus on particular aspects of your business?
- Threats and Responses: If you discover threats to your business, how will you respond?
Once you conclude an audit, you’ll have a clearer picture of how safe (or otherwise) your business is from cyber threats. And if you discover any threats, you can take action to neutralize them.
Follow Cybersecurity Tips to Safeguard Business Data
If you want to keep your business data safe, you’ll need to implement two or more of the cybersecurity best practices discussed in the article. The statistics are clear that cybercrime is on pace to skyrocket in the future, which means that businesses need to be prepared.
To recap, consider enabling two-factor authentication and enforcing a strong password policy. Back up your data regularly and train your employees about cybersecurity to reduce risks caused by human error. Finally, conduct regular cybersecurity audits to stay up-to-date on your business’s security from cyber threats.
Find cybersecurity experts that can protect your business data from attackers. Connect with a cybersecurity company on The Manifest.
